Orthopaedic Department
On this page
Download leaflet
Bow Legs Knock Knees Flat Feet and In-Toing Leaflet PIAG 37 (303kB)
Why does my child in-toe?
In toeing is common in young children, there are three main causes
- Hooked Foot: This is due to the position of the baby in utero. It can take a number of years to correct. Children do not need to have special footwear.
- Twist in lower leg (tibial torsion): This is an inward twist of the bone in the lower leg. Most straighten with normal development over a number of years. Wearing splints or exercises do not help.
- Twist in thigh (femoral anteversion): This is an inward twist of the upper leg bone. It is most noticeable at age five or six years. It is usually gone when the child is age 10 years old. Most correct with normal development. Wearing splints or exercise do not help.
Why does mu child have bow legs (Genu Varum)?
In their first year all children are bow legged.
Their legs gradually straighten out during their second year
No treatment is needed as the changes happen naturally
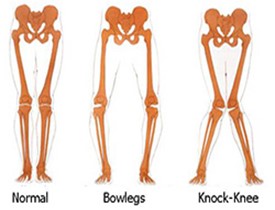
Why does my child have knock knees (Genu Valgum)?
It is in their 2nd and 3rd years children become knock-kneed and both legs are usually the same.
This is common in toddlers up to school age and both legs are usually the same. The weight of children with knock knees is often higher than the average weight.
Children with knock knees may not run well or may look awkward. They may walk on the inside border of their feet and complain of aching feet. Most children with knock knees improve without treatment.
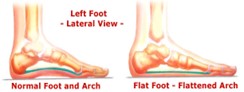
Why does my child have flat feet?
Flat feet are normal in infants, children and adults. Just as children are of different heights, arches have different heights too. One in five children never develops an arch.
Most children have low arches because they are loose jointed. The arch flattens when they are standing, and their feet seem to be rolled in and pointed outward. The arch can be seen when the child stands on their toes.
A doctor would be concerned if the flatfoot is stiff / rigid, painful or very severe.
Special shoes, inserts, wedges or exercises Illustration showing normal and full arched feet
do not create an arch in a child with a flexible flat foot. Wearing a pad or insert under the
arch of a simple flexible flatfoot can make the child less comfortable.
Most adults with flexible flat feet have strong, pain free feet.
Shoes for Children
Barefoot people have the best feet! However a child’s foot needs protection from cold and sharp objects. Your child needs to wear a flexible, soft shoe that allows maximum freedom for the foot to develop normally. Stiff, ‘supportive’ shoes are not good for feet because they limit movement needed for developing strength and retaining foot mobility.
This leaflet only gives general information. You must always discuss the individual treatment of your child with the appropriate member of staff. Do not rely on this leaflet alone for information about your child’s treatment.
This information can be made available in other languages and formats if requested.
PIAG: 37